Folic Acid Vitamin B9 feed additives for poultry

animal feed addictive L-Lysine HCl 98.5% feed grade amino acids
February 17, 2017
Folic acid fine powder Vitamin B9 feed addictive for cattle
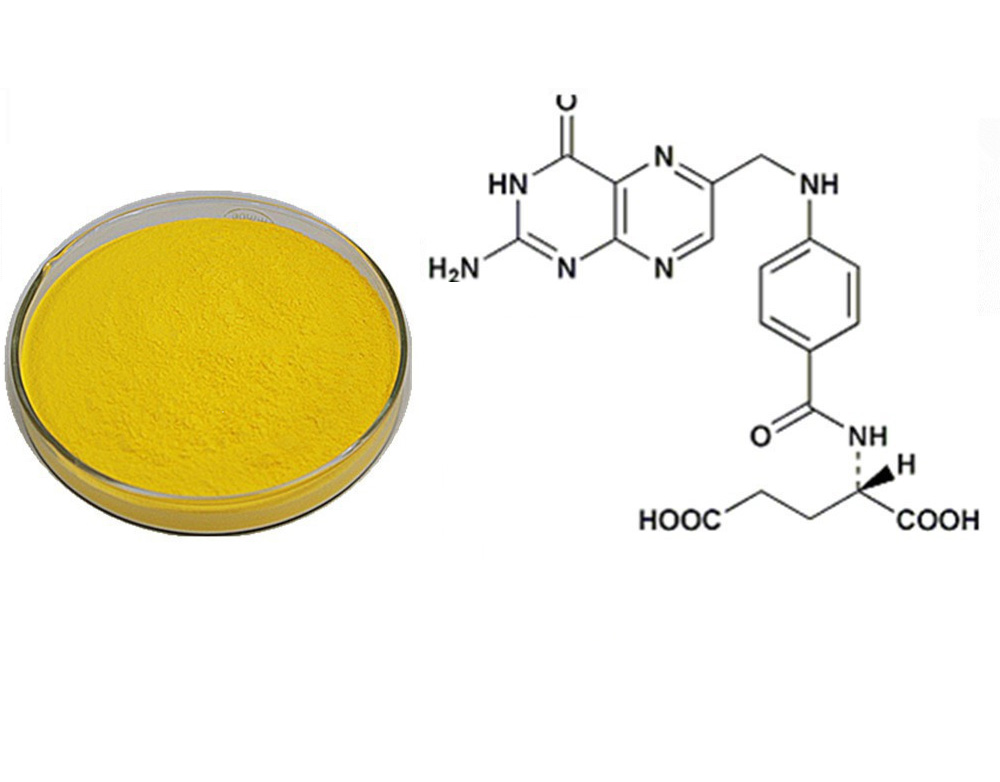
March 7, 2017Folic acid is one of the B vitamins and is likewise referred to as vitamin B9. It is discovered in different forms in typical foods, specifically green, leafy veggies.
Folic acid and folate are both terms utilized to describe this vitamin. Folic acid describes the chemical substance, pteroylmono glutamic acid, which is commonly used as a vitamin supplement. Folate is the general term used to refer to any of the protein-bound or other conjugated types of folic acid, which are types generally found in foods.
The body readily takes in as much as 90 percent of folic acid (the form found in supplements). Folate or protein-bound folic acid substances can not be soaked up till they are customized by enzymes in the body. As little as 50 percent of folate can be taken in.
Folic shortage results in megaloblastic anemia.
The biological functions of folate all originate from the functions of folate coenzymes in one-carbon metabolic process. Folate coenzymes mediate transfer of one carbon units (methyl or methylene groups) in biochemical reactions.
Folate coenzymes are vital for nucleic acid metabolism in two methods: synthesis of DNA and synthesis of methionine.
Folic acid plays a role in the biosynthesis of heme and hemoglobin.
Folate coenzymes are required for the conversion of histidine to glutamic acid and serine to glycine.
Folate is essential for development of red and leukocyte from stem cells in bone marrow and for their maturation.
| SPECIFICATION OF FOLIC ACID FOOD GRADE USP38 | |
| Appearance | Yellow, yellow-brownish or yellowish-orange, crystalling powder |
| Ultravlolet Absorption | A256/A365=2.80∼3.00 |
| Related Compounds | ≤2.0% |
| Water | ≤8.5% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.3% |
| Assay | 97.0-102.0%(on anhydrous substance) |
| Conclusion | The product conforms to the standard of USP38 |
| Storage condition | Kepp away from sunlight, sealed in dry place under room temperature |






2 Comments
What is the use of folic acid in poultry?
Folic acid must be present in the feed to improve oviduct development, egg FA content, hatchability, weight gain, chick body weight, initial average body weight, feed intake, relative growth rate, appropriate breast fillet percentage, and decrease FCR and white striping score.